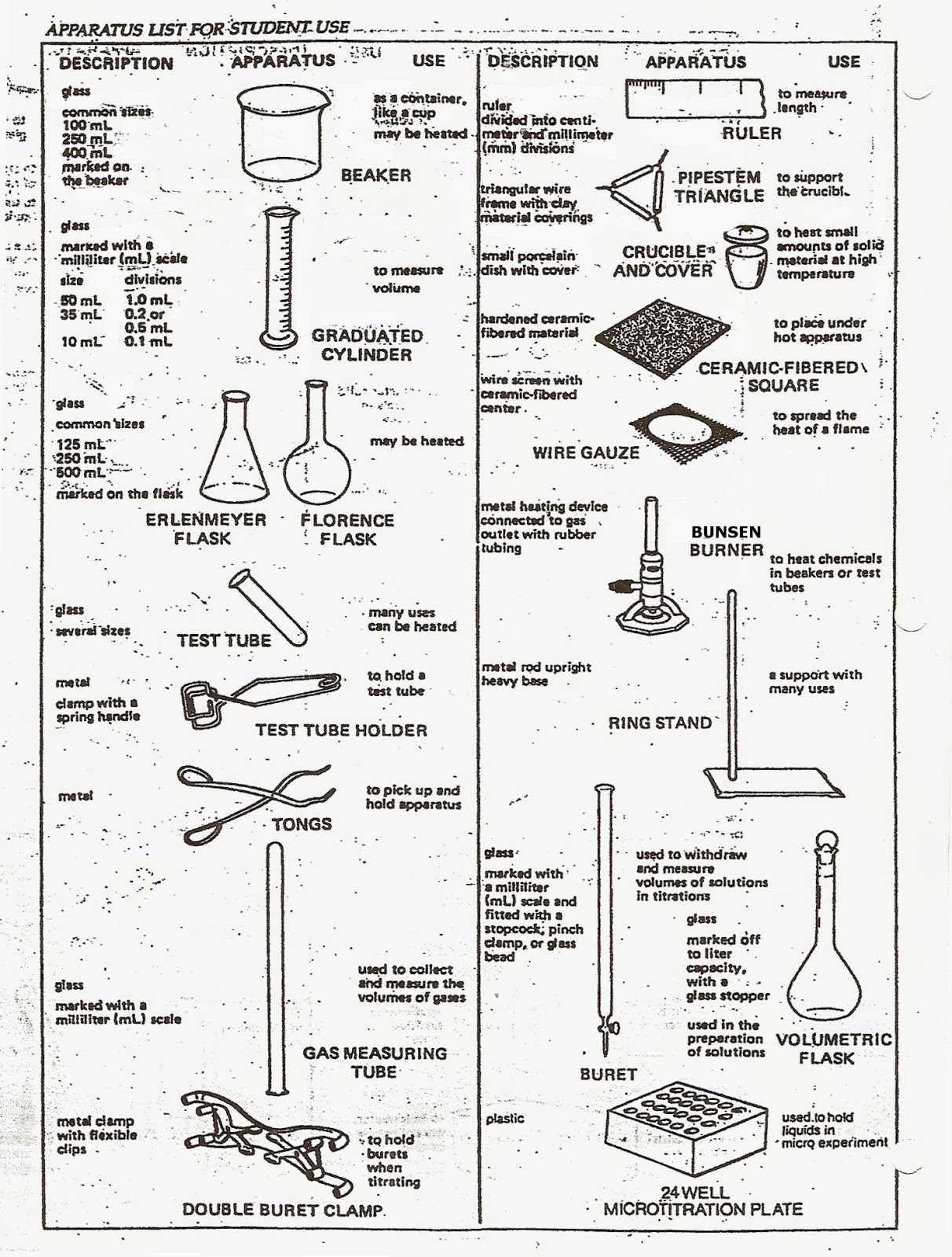
Chemistry Equipment Names: A Comprehensive Guide To Lab Tools
Chemistry equipment names play a crucial role in the world of science, particularly in laboratories where precision and accuracy are paramount. Understanding the various tools and their functions can significantly enhance the efficiency of experiments and research. In this article, we will explore the essential chemistry equipment names, their uses, and how they contribute to successful scientific inquiries.
From basic instruments like beakers and test tubes to more complex apparatus like spectrophotometers and chromatographs, each piece of equipment serves a unique purpose. This comprehensive guide will delve into the most commonly used chemistry tools, providing insights into their designs, functionalities, and the contexts in which they are employed. Whether you are a student, educator, or professional chemist, this article aims to be a valuable resource for anyone looking to enhance their knowledge of laboratory equipment.
In addition to discussing the names and uses of various chemistry equipment, we will also touch upon the importance of safety measures in the lab and best practices for handling these tools. By the end of this article, you will have a well-rounded understanding of chemistry equipment names and their significance in scientific research.
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Chemistry Equipment
- 2. Commonly Used Chemistry Equipment
- 3. Specialized Laboratory Instruments
- 4. Safety Equipment in Chemistry Labs
- 5. Maintenance and Care of Laboratory Equipment
- 6. Innovations in Chemistry Equipment
- 7. Conclusion
- 8. References
1. Introduction to Chemistry Equipment
Chemistry equipment encompasses a wide range of tools and instruments that are essential for conducting experiments and research in chemistry. These tools aid in measuring, mixing, heating, and analyzing substances, allowing chemists to explore the properties and reactions of different materials. Understanding the correct names and uses of these instruments is vital for ensuring accurate results and maintaining safety in the laboratory.
2. Commonly Used Chemistry Equipment
In this section, we will cover some of the most commonly used chemistry equipment names and their functions:
2.1 Beakers
Beakers are cylindrical containers with a flat bottom, typically made of glass or plastic. They are used for mixing, heating, and holding liquids. Beakers are marked with measurement lines to indicate volume.
2.2 Test Tubes
Test tubes are narrow glass or plastic tubes used to hold small quantities of liquids or solids. They are often used in experiments to mix substances and observe reactions.
2.3 Pipettes
Pipettes are slender tubes used to transfer small volumes of liquid accurately. There are various types of pipettes, including graduated pipettes and micropipettes.
2.4 Burettes
Burettes are long, graduated tubes with a stopcock at the bottom, used for delivering precise volumes of liquid in titration experiments.
2.5 Flasks
Flasks, such as Erlenmeyer and volumetric flasks, are used for mixing, heating, and storing liquids. Their unique shapes help minimize evaporation and allow for easy swirling of contents.
2.6 Funnels
Funnels are used to transfer liquids or fine-grained substances into containers with small openings. They help reduce spills and improve accuracy during transfers.
2.7 Hot Plates
Hot plates are electrical devices used to heat substances in laboratory settings. They provide a controlled heat source for various experiments.
2.8 Mortar and Pestle
A mortar and pestle are used to grind and mix solid substances into a fine powder, essential for preparing samples for analysis.
3. Specialized Laboratory Instruments
Advanced research requires specialized instruments that offer greater precision and capabilities. Here are some essential instruments used in chemistry labs:
3.1 Spectrophotometers
Spectrophotometers measure the intensity of light absorbed by a sample at different wavelengths. They are crucial for quantitative analysis in chemistry.
3.2 Chromatographs
Chromatographs are used for separating and analyzing mixtures. Techniques like gas chromatography (GC) and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) are commonly employed in analytical chemistry.
3.3 Centrifuges
Centrifuges separate components of a mixture based on density by spinning samples at high speeds. They are widely used in biochemical and clinical laboratories.
3.4 pH Meters
pH meters are electronic devices that measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. They provide accurate readings essential for various chemical analyses.
4. Safety Equipment in Chemistry Labs
Safety is paramount in any laboratory setting. Here are some key safety equipment items that every chemist should be familiar with:
4.1 Safety Goggles
Safety goggles protect the eyes from hazardous chemicals and splashes during experiments.
4.2 Lab Coats
Lab coats provide a barrier between the skin and harmful substances, reducing the risk of chemical exposure.
4.3 Gloves
Chemical-resistant gloves protect the hands from corrosive and toxic substances.
4.4 Fume Hoods
Fume hoods are ventilated enclosures that remove hazardous fumes and vapors, ensuring a safe working environment.
5. Maintenance and Care of Laboratory Equipment
Proper maintenance and care of laboratory equipment are essential for ensuring accuracy and longevity. Here are some best practices:
- Regularly clean all equipment after use to prevent contamination.
- Calibrate instruments periodically to maintain accuracy.
- Store equipment in designated areas to prevent damage.
- Check for any signs of wear or malfunction and address them promptly.
6. Innovations in Chemistry Equipment
The field of chemistry is continually evolving, with new technologies and innovations enhancing research capabilities. Some notable advancements include:
6.1 Automated Analyzers
Automated analyzers streamline the process of chemical analysis, increasing efficiency and accuracy in laboratories.
6.2 Smart Lab Equipment
Smart technologies enable remote monitoring and control of laboratory instruments, allowing for greater flexibility and data management.
6.3 Eco-Friendly Equipment
Innovations in eco-friendly lab equipment focus on reducing chemical waste and energy consumption, promoting sustainability in research.
7. Conclusion
In conclusion, knowledge of chemistry equipment names is essential for anyone involved in scientific research. Understanding the functions and proper usage of various tools can significantly enhance the quality of experiments and ensure safety in the laboratory. We encourage readers to explore further, share their thoughts in the comments, and engage with additional resources on chemistry.
8. References
For more information, check the following reputable sources:
Exploring The Creative World Of Bo Welch: A Master Of Set Design And Direction
Jaime Bergman: The Journey Of A Multifaceted Star
Exploring The Life And Career Of Jimmy McNichol: A Timeless Star